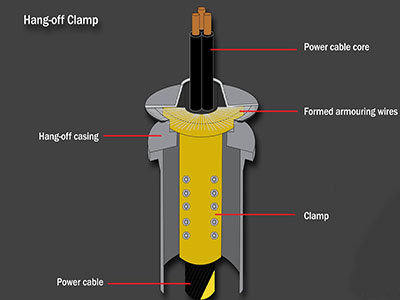
Inter-array cable buoyancy refers to systems designed to support and control the position of submarine inter-array cables used in offshore wind farms, oil and gas fields, and other subsea installations. These cables connect multiple offshore units—such as wind turbine generators—to a central offshore substation, where the generated power is transmitted to shore.
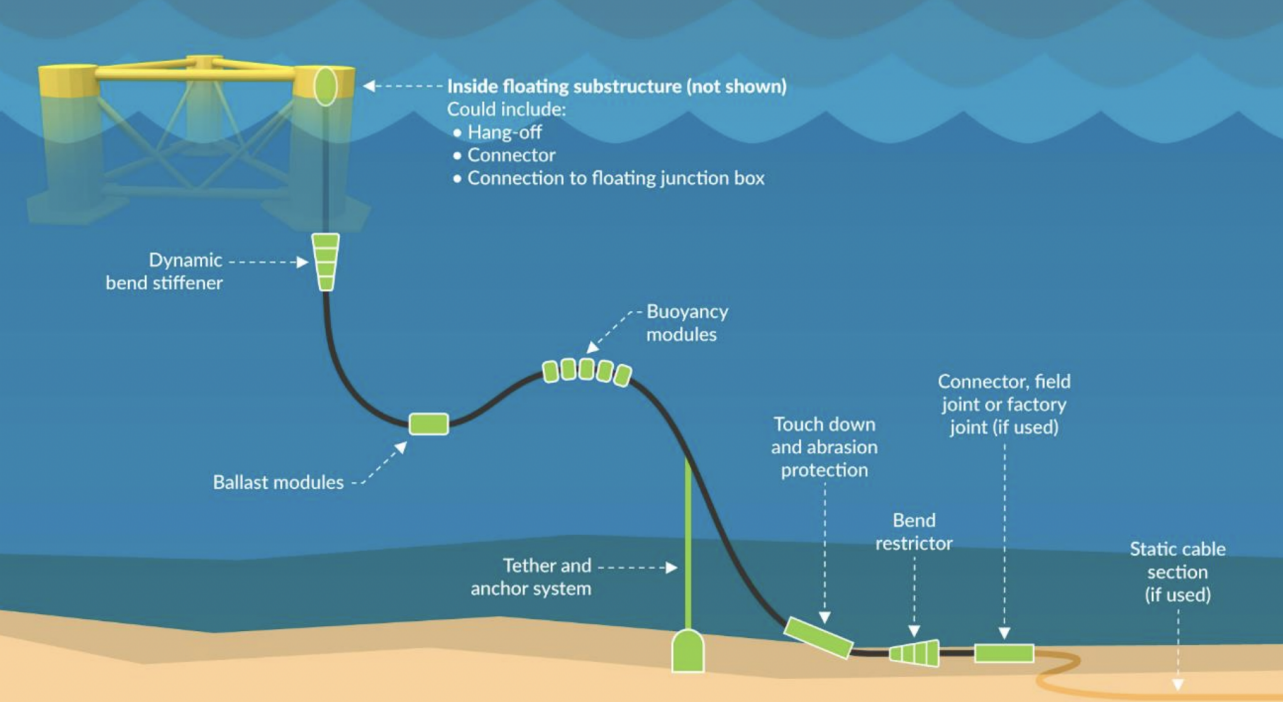
In dynamic subsea environments, cables are exposed to waves, currents, seabed abrasion, and movement caused by floating structures. Without proper buoyancy management, cables may experience excessive bending, fatigue, or contact with the seabed, leading to costly damage and downtime.
What is a buoyancy block?
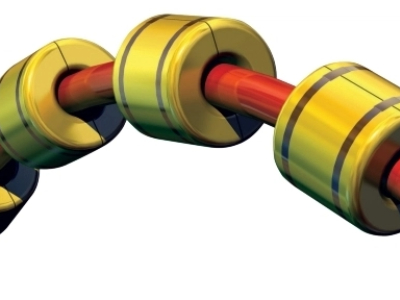
A buoyancy block is a specially designed flotation module, typically made from high-performance syntactic polyurethane foam, that attaches to subsea cables to provide controlled uplift. By adjusting the spacing and quantity of buoyancy blocks, engineers can achieve the desired cable configuration—often a lazy wave or steep wave profile—that reduces strain and extends cable service life.
Key functions of buoyancy blocks
Cable protection: Prevents cables from dragging on the seabed or being damaged by abrasion.
Stress reduction: Maintains optimal bend radius and minimizes tension from currents and vessel movement.
Stability: Helps maintain a controlled midwater suspension, improving cable performance and longevity.
Versatility: Can be adapted for various cable diameters and subsea depths.
Applications
Offshore wind farms – supporting inter-array cables between turbines and substations.
Oil & gas production – managing flexible risers, umbilicals, and flowlines.
Marine energy projects – protecting power cables in wave and tidal energy systems.
By integrating buoyancy blocks into subsea cable layouts, project developers can ensure safer operations, lower maintenance costs, and longer service life for critical offshore power infrastructure.