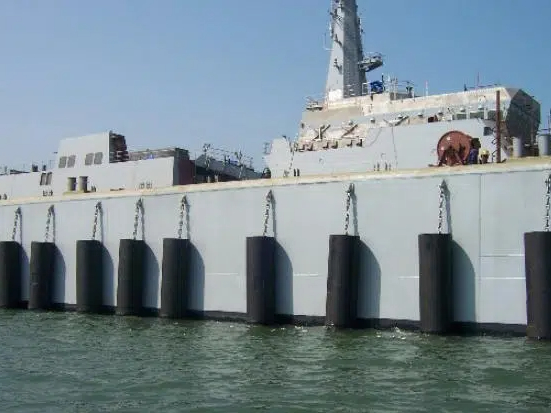
Marine fenders, also known as ship protection fenders, are essential safety devices designed to absorb impact energy during vessel berthing and mooring operations. They protect both the ship’s hull and quay structures, ensuring safe docking under various sea conditions.

Functions of marine fenders
• Impact energy absorption: Reduce collision force between the vessel and the dock, or between two ships during side-by-side mooring.
• Hull protection: Prevent dents, scratches, or structural damage to the vessel’s side.
• Safety enhancement: Ensure smooth and stable boarding, cargo handling, and offshore operations.
• Durability in harsh environments: Withstand seawater corrosion, UV exposure, and repeated compression.
Installation scenarios & locations
Marine fenders can be installed in various offshore and port environments, depending on operational needs:
• Ship-side installation
Along the side shell of the vessel to protect against quay walls or other ships during mooring.
At boarding areas where gangways or ladders connect to the vessel.
• Dock and pier installation
On quay walls, dolphins, and berthing structures are used to absorb the impact of berthing.
At cargo terminals and passenger ports, to ensure safe docking of different vessel types.
• On buoys
In locations where mooring buoys are used, marine fenders can be incorporated into the buoy design to protect vessels when they are anchored to the buoys.
• Offshore platforms
Around oil & gas platforms, floating production units (FPSOs), and wind farm service platforms, where supply ships frequently berth.
• Special areas
Tugboats and workboats: Fenders installed around the bow, stern, and sides for pushing operations.
Ship-to-ship transfer areas: Installed on vessel hulls to avoid direct steel-to-steel contact.
Typical installation methods
Bolted fixing plates for dockside or hull installation
Chain or rope suspension for floating fenders
Integrated brackets or embedded fixtures for offshore structures.