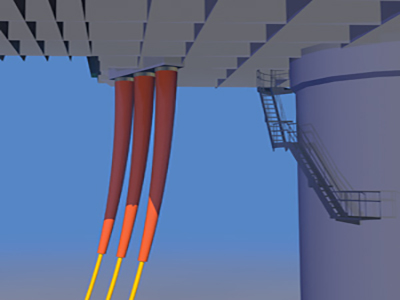
Floating offshore wind farms operate in deep waters where wind turbines are mounted on floating platforms rather than fixed foundations. These platforms are connected to the subsea export network by dynamic cables, which must carry high-voltage electricity while enduring constant movement from waves, currents, and wind.
What is a dynamic cable?
A dynamic cable is a specially designed subsea power cable capable of withstanding mechanical stresses caused by floating platform motion. It consists of:
Hang-off point – the secure connection between the cable and the floating platform.
Bend protection – bend stiffeners or bend restrictors to prevent excessive bending near the termination.
Midwater section – the suspended portion between the platform and seabed, exposed to hydrodynamic forces.
Touchdown zone (tdz) – the area where the cable meets the seabed, vulnerable to fatigue and abrasion.
The role of buoyancy in dynamic cables
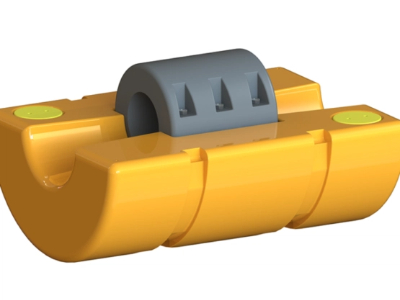
In harsh marine environments, uncontrolled cable motion can lead to premature wear and failure. Dynamic cable buoyancy is achieved by attaching buoyancy blocks—modular flotation units—to the cable’s midwater section. This creates a controlled, lazy wave or steep wave configuration, delivering key benefits:
Fatigue reduction – absorbs platform-induced motion, reducing stress on the TDZ.
Bend radius control – prevents sharp bending that can damage conductors and insulation.
Seabed clearance – keeps the cable off the seabed to avoid abrasion and scour.
Load distribution – spreads mechanical stresses along the cable for a longer service life.
Why it matters for offshore wind
Buoyancy systems are a critical element in ensuring the safety, reliability, and operational efficiency of floating wind power cables. By managing motion and mechanical loads, they protect high-value infrastructure, minimize maintenance costs, and extend the service life of subsea electrical connections, contributing to the overall success of floating offshore wind projects.